In a GUI, checking the state of a network interface card is pretty easy. That is to say, you just have to click on the network information icon to see all the details. On the other hand, do you ever wonder how to check it in Linux command line? It is really simple task if you use mii-tool command. Mii-tool gives you the following features:
- View and modify network interface configurations
- Control the links
- Set auto-negotiation mode
- Set duplex modes
In this guide, I’ll show you how to use this tool to get the most out of it.
Step 01 : Installation
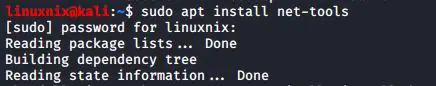
You can install the mii-tool using the following command.
#sudo apt install net-tools
Step 02 : Check a Single Interface
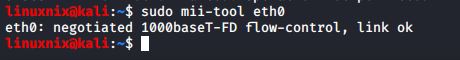
To see the information on a specific interface, run the following command.
#sudo mii-tool <interface_name>
However if no interface is specified, then it will check all available interfaces. In other words, it will check all interfaces from eth0 to eth7.
Step 03 : See Detailed Information
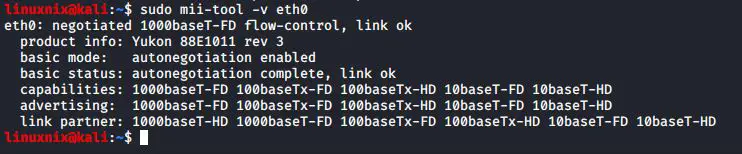
You can see detailed information on each card using -v option.
#sudo mii-tool -v <interface_name>
Step 04 : Set Network Interface Speed
To set the speed of the interface manually, use the following command.
#sudo mii-tool –force <option>
For example, here I have specified the speed of the eth0 interface to 10 Mbit.
Step 05 : Restart Auto-Negotiation
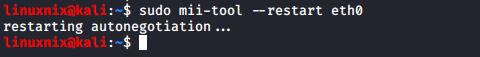
Network devices use an auto-negotiation protocol to communicate the technologies they support. It will then select the fastest mutually supported technology. To restart the auto-negotiation of the interface, run the following command.
#sudo mii-tool –restart <interface_name>
Step 06 : change the duplex mode
You can change the duplex mode in the interface using the -F option.
#sudo mii-tool -F <option> <interface_name>
For example, here I have set the speed of the eth0 interface to 10 Mbps and the duplex mode to half-duplex.
Step 06 : report link status changes
Run the following command to watch a single interface and report changes in the link status. That is to say, the interfaces are listed at one second intervals by default.
#sudo mii-tool -w <interface>
Step 07 : report link status
With the use of -l option, mii-tool will record link status changes in the system log instead of showing in the screen.
#sudo mii-tool -l <interface_name>
Step 08 : Reset the configurations
Most importantly, you should be able to reset it to its default configuration if something goes wrong. For that, run the following command
#sudo mii-tool -R <Interface_name>
In conclusion, the mii-tool is a useful utility to check and modify your NIC from the command line. Also, make sure to check this article to learn how to view many different network statistics using netstat command.