The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe. Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix.
File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others.
This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level of access to a file/folder for the users who access them.
Why we need to change permissions of a file/directory?
1) To execute a script.
2) File access required by an application to work properly.
3) To make a file editable by a user.
How can we change permissions for a file/directory?
Permission/access is either Executable or Writable or Readable for a file/folder and can be changed by using following methods
1) Numerical method: Specifying numbers (1, 2, and 4,) to change the permission for a file/folder
2) Alpha method: Using alphabets (w, x, r, u, o, g, a, -, +, =, s, t) to change permissions for a file/folder
Numerical method
2^0=1 --eXecute 2^1=2 --Write 2^2=4 --Read
Addition to this there are three more concepts which are linked to this numbering method (I SUID, SGID, Sticky Bit). We will explain about these things in coming posts.
Alpha method
w --Write x --eXecute r --Read u --User g --Group o --Others a --all + --Add specified permissions to the mention user/group/others/all - --Remove specified permissions from the mention user/group/others/all = --Replicate the permission to other class of the group/user/others.
Addition to these there are s and t permissions(SUID, SGID and Sticky Bit) available for chmod command which we will discuss in next chmod tutorial.
In this post we will see numerical method as well as alpha method to change the basic permissions of a file. For that you should understand ls command output.
ls -al
Total 36
drwx------ 2 surendra surendra 4096 May 18 07:32 .
drwxr-xr-x 691 root root 12288 May 26 11:34 ..
-rw------- 1 surendra surendra 305 May 18 11:09 .bash_history
-rw-r–r–
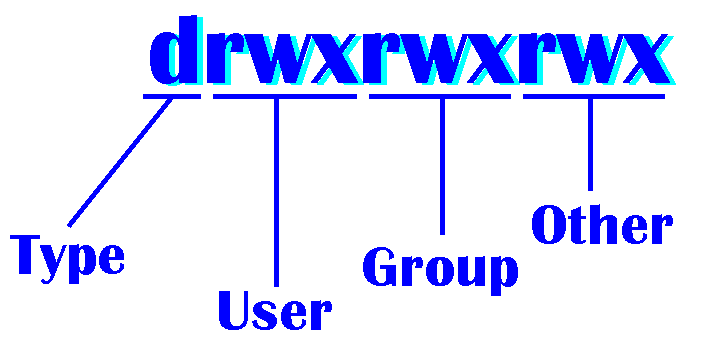
The first column of the ls -l output can be divided in to 2 parts as shown above(in black[-] and red[rw-r–r–]).
1) File type (you can refer our other tutorial for different file types available in Linux)
2) Permissions to the file
This one again divided in to 3 parts
A) User permissions: This will show what the permissions an owner gets are
B) Group permissions: This will show what the permissions a group where owner belongs gets are.
C) Others permissions: This will show what the permissions all other users get are.
-rw-r–r–
The above permissions which can be divided as
rw- For the owner
r– For the group where user belongs
r– For all other users
chmod syntax: Before adding any permissions we have to what’s the syntax of chmod command
chmod options file/folder
For more help on chmod you can give below command
man chmod
Adding permission for User with examples
Through Numerical method:
Example 1: The file should have read, write and execute permissions to user, read and execute permissions to group and read, and execute permissions to others.
read, write and execute permissions to user =7
read and execute permissions to group =5
read and execute permissions to others=5
So total permissions will be 755
chmod 755 filename
Example 2: Providing write access to a user
chmod u+w filename
Example 3: Adding write permissions to a group
chmod g+w filename
Example 4: Adding executable permissions to others
chmod o+x filename
Example 5: Adding executable and write permissions to all
chmod a+wx filename
Example 6: Replicating user permissions to a group
chmod u=g filename
Example 7: Removing execute permissions to a user
Chmod u-x filename
Example 8: Adding execute permissions to others
Chmod o+x
Explore your self on how to use other options. In the next post we will see more about chmod options and examples such as change file/folder permissions recursively, SUID, SGID and Sticky bit. And we will see practical usages of chmod too.